WORLD OF DIABETES

WHAT IS DIABETES
Diabetes is a chronic disease that occurs when the pancreas is no longer able to make insulin, or when the body cannot make good use of the insulin it produces. Insulin is a hormone made by the pancreas that acts like a key to let glucose from the food we eat pass from the blood stream into the cells in the body to produce energy. All carbohydrate foods are broken down into glucose in the blood. Insulin helps glucose get into the cells.
Not being able to produce insulin or use it effectively leads to raised glucose levels in the blood (known as hyperglycemia). Over the long-term high glucose levels are associated with damage to the body and failure of various organs and tissues.
Read More
TYPES OF DIABETES
There are three main types of diabetes - type 1, type 2 and gestational.
- Type 1 diabetes can develop at any age, but occurs most frequently in children and adolescents. When you have type 1 diabetes, your body produces very little or no insulin, which means that you need daily insulin injections to maintain blood glucose levels under control.
- Type 2 diabetes is more common in adults and accounts for around 90% of all diabetes cases. When you have type 2 diabetes, your body does not make good use of the insulin that it produces. The cornerstone of type 2 diabetes treatment is healthy lifestyle, including increased physical activity and healthy diet. However, over time most people with type 2 diabetes will require oral drugs and/or insulin to keep their blood glucose levels under control. Learn more
- Gestational diabetes (GDM) is a type of diabetes that consists of high blood glucose during pregnancy and is associated with complications to both mother and child. GDM usually disappears after pregnancy but women affected and their children are at increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
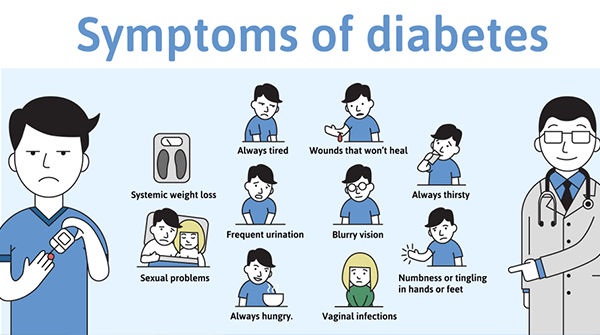
SYMPTOMS OF DIABETES
The symptoms of type 2 diabetes are similar to those of type 1 diabetes and include:
- Excessive thirst and dry mouth.
- Frequent urination.
- Lack of energy, tiredness.
- Slow healing wounds.
- Recurrent infections in the skin.
- Blurred vision.
- Tingling or numbness in hands and feet.

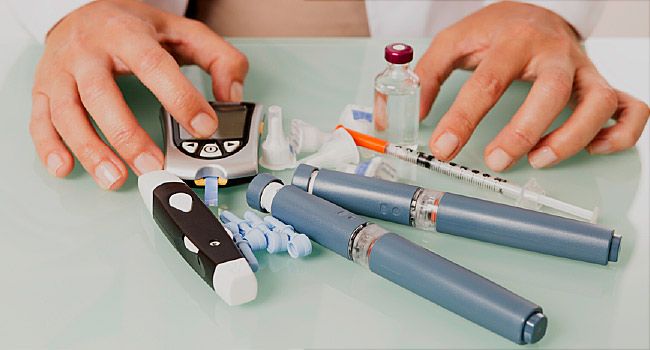
DIABETES TESTS
Here are 4 crucial tests that both people with diabetes and non-diabetic people benefit from
- Random Blood Glucose Test
- Fasting Blood Glucose Test
- Postprandial Blood Glucose Test
- HbA1c Test
- All the above mentioned tests can be done at a diagnostic center, or via home sample collection
- For home sample collection, search the internet with "Diabetes blood test near me" to get a list of service providers
- For random blood glucose test, blood sample can be given at any time of the day and there is no need for fasting
- For fasting blood glucose test, a fasting period of 8 hours is required. In this period, one shouldn't eat or drink anything except for water
- Blood sample for postprandial blood glucose test is taken 2 hours after consuming food
- HbA1c test does not need any fasting and sample can be given at any time of the day
- One can also get their fasting and postprandial tests done at home using a diabetes blood sugar test kit. This includes a glucometer, a lancet, and test strips.
DIABETES TREATMENT
The cornerstone of managing type 2 diabetes is a healthy lifestyle, which includes a healthy diet, regular physical activity, not smoking, and maintaining a healthy body weight.
Over time, a healthy lifestyle may not be enough to keep blood glucose levels under control and people with type 2 diabetes may need to take oral medication. If treatment with a single medication is not sufficient, combination therapy options may be prescribed.
When oral medication is not sufficient to control blood glucose levels, people with type 2 diabetes may require insulin injections.
The first question a person asks after being diagnosed with type 2 diabetes is "do I have to take medicines lifelong?" The fact of the matter remains that one has to take diabetes medications lifelong. There is no escaping from this fact - diabetes drugs are now your friends along with a diabetes diet plan and of course, the walking shoes.
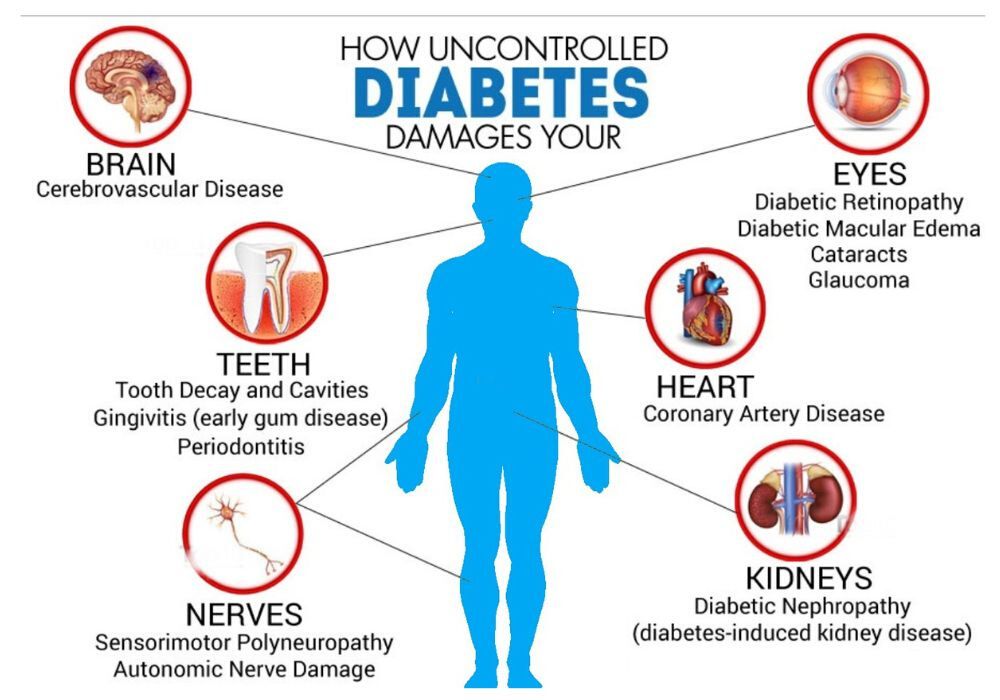
DIABETES COMPLICATIONS
People with diabetes have an increased risk of developing a number of serious health problems. Consistently high blood glucose levels can lead to serious diseases affecting the heart and blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, nerves and teeth. In addition, people with diabetes also have a higher risk of developing infections. In almost all high-income countries, diabetes is a leading cause of cardiovascular disease, blindness, kidney failure, and lower limb amputation.
Maintaining blood glucose levels, blood pressure, and cholesterol at or close to normal can help delay or prevent diabetes complications. Therefore people with diabetes need regular monitoring.

DIABETES PREVENTION
At present, type 1 diabetes cannot be prevented. The environmental triggers that are thought to generate the process that results in the destruction of the body's insulin-producing cells are still under investigation.
While there are a number of factors that influence the development of type 2 diabetes, it is evident that the most influential are lifestyle behaviours commonly associated with urbanization. These include consumption of unhealthy foods and inactive lifestyles with sedentary behaviour. Studies from different parts of the world have established that lifestyle modification with physical activity and/or healthy diet can delay or prevent the onset of type 2 diabetes.
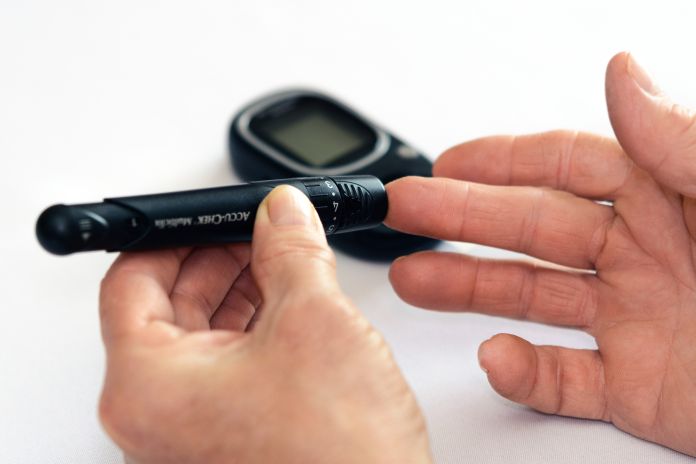
DIABETES CARE @ HOME
Regularly monitoring blood sugar levels at home offers a thorough insight into one's health.
Monitoring your blood sugar levels at home at given intervals provides an insight to help determine if you are at a risk of developing any potential diseases associated with diabetes in the near future
Type 2 diabetes is closely associated with a dangerous risk of coronary heart disease. It arises from dyslipidemia that develops in type 2 diabetes. Diabetic dyslipidemia is characterized by a decrease in HDL cholesterol levels and increase in triglyceride levels.
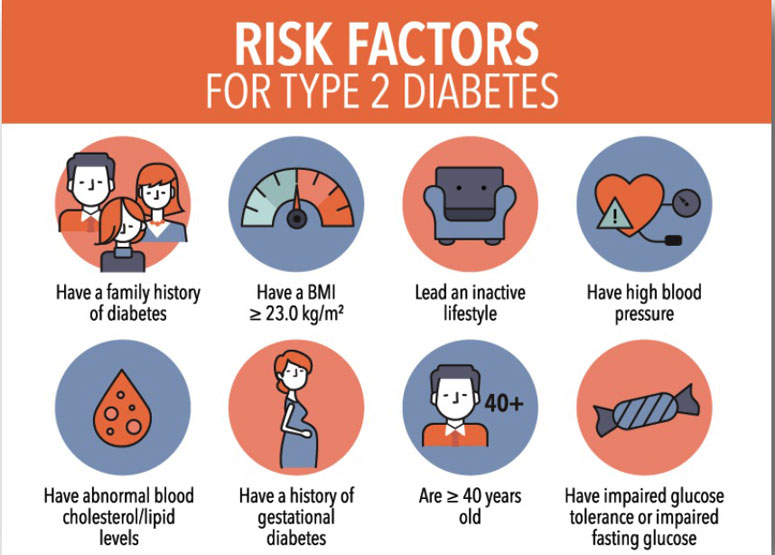
DIABETES RISK ASSESSMENT
The good news is you can prevent or delay type 2 diabetes
That's right: If you're at risk, making small changes to the way you eat, increasing your physical activity levels or getting early treatment can, for some, actually return blood sugar levels to a normal range. So, take a breath-and then take action
If you're looking for ideas on how to get started-or reverse the course of what's already underway-we have everything you need. Our risk test can help you assess your risk level. And if you're at high risk or feel like you might have diabetes, get a blood test to find out if you have diabetes or prediabetes.

Body Mass Index(BMI) Calculator
